The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a travel notice for people going to Rwanda due to a Marburg Virus Disease (MVD) outbreak, the first ever in the country.
The Ministry of Health of the Republic of Rwanda declared a Marburg virus disease (MVD) outbreak on 27 September 2024. Since then, and as of October 1, 29 confirmed cases and 10 deaths have been reported.
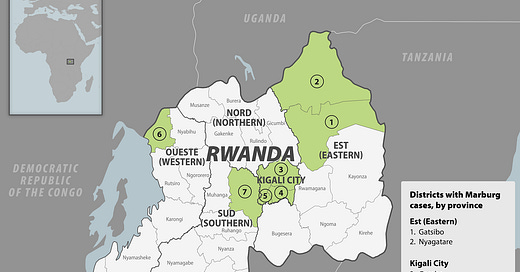
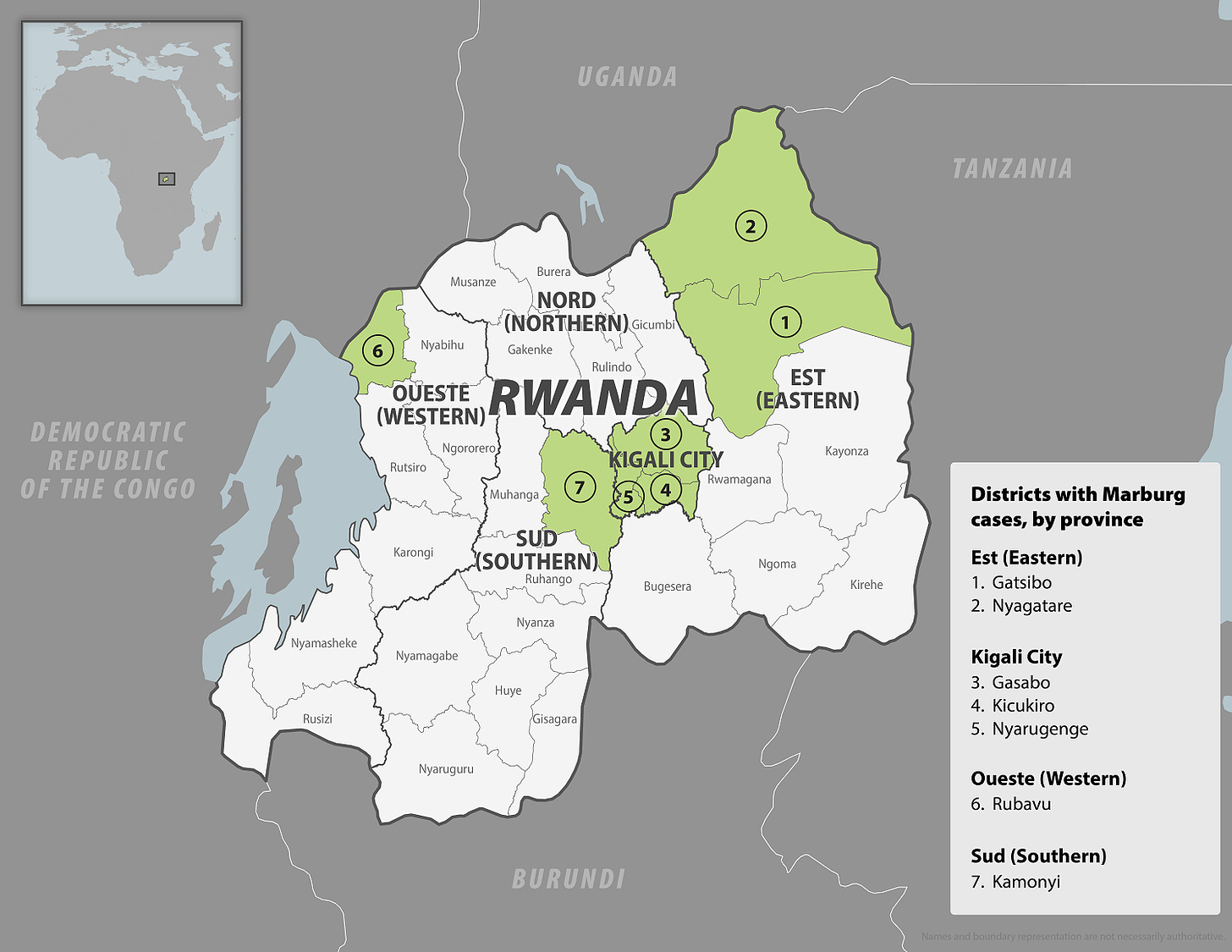
Cases are reported in seven out of the 30 districts in the country-(see map).
CDC offers the following advice for travelers to Rwanda:
Consider getting travel insurance before you travel, including health and medical evacuation insurance, to cover yourself in case delays, injuries, or illnesses occur on your trip.
Avoid contact with sick people who have symptoms, such as fever, muscle pain, and rash.
Avoid contact with blood and other body fluids.
Avoid visiting healthcare facilities in the outbreak area for nonurgent medical care or for nonmedical reasons.
Avoid contact with dead bodies or items that have been in contact with dead bodies, participating in funeral or burial rituals, or attending a funeral or burial.
Avoid visiting traditional healers.
Avoid contact with fruit bats or entering the caves and mines where they live.
Avoid nonhuman primates (e.g., chimpanzees, gorillas).
Watch your health for symptoms of Marburg while in the outbreak area and for 21 days after leaving the outbreak area.
If you develop fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, rash, chest pain, sore throat, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, or unexplained bleeding or bruising, you should separate yourself from others (isolate) and seek medical care immediately.
Marburg virus disease (Marburg) is a rare and deadly disease that has, at times, caused outbreaks in several African countries. The disease is named after the city in Germany where it was first reported in 1967.
Marburg is spread by contact with blood or body fluids of a person infected with or who has died from Marburg. It is also spread by contact with contaminated objects (such as clothing, bedding, needles, and medical equipment) or by contact with animals, such as bats and nonhuman primates, who are infected with Marburg virus.
Marburg is a viral hemorrhagic fever. Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, rash, chest pain, sore throat, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, and unexplained bleeding or bruising.
Infection with Marburg virus is often fatal. There are no approved vaccines or treatments for Marburg.