The National Institute of Public Health (NIPH), or Statni Zdravotni Ustav (SZU) in the Czech Republic is reporting a rise in scabies infestations in the Vysočina region, where regional hygienists recorded fifty infections last month, including schoolchildren.
Officials also report cases in other parts of the country.
"In the Vysočina Region, we have also observed a more frequent occurrence of scabies in recent years. The increase in the number of diseases in society is contributed by a decrease in our immunity, collective hypersensitivity, travel, poor social and hygienic standards, and promiscuity. Scabies is usually spread directly, for example, through close contact with the skin of a sick person, or indirectly, especially through contact with contaminated bed linen, towels, and clothing. Scabies is easily spread between partners and family members or in large groups," says MUDr. Hana Pavlasová, Director of the Department of Anti-Epidemic KHS of the Vysočina Region. "However, infection is usually not possible during normal daily contact. There is no need to worry that scabies would appear in our country due to mere touch or a normal handshake," adds MUDr. Pavlasová.
Problems with this highly contagious disease are being addressed, for example, in the Humpolec children's home and the local Hálkova elementary school, where several children were infected. All classes at the school were disinfected and hygiene measures are also in place in the families of schoolchildren. Scabies does not avoid other places, so vigilance is appropriate.
Scabies: Ivermectin use in mass drug administration
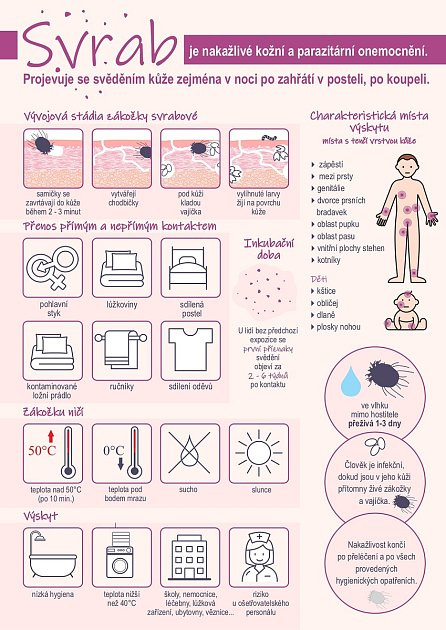
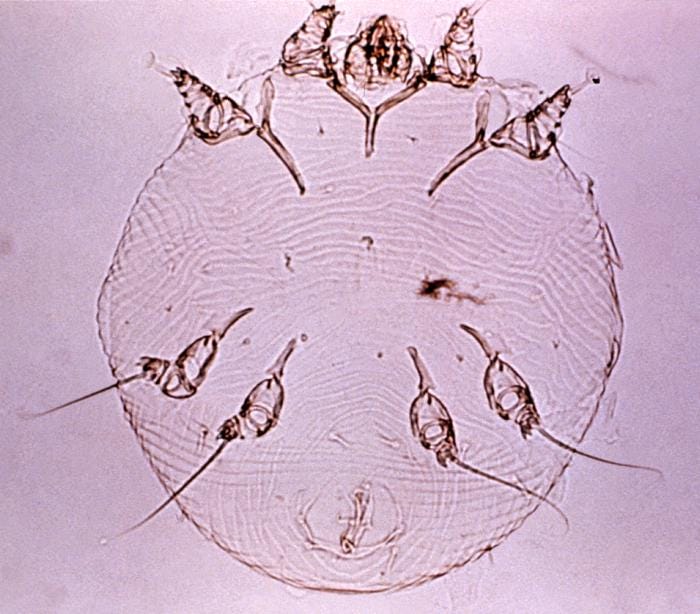
Scabies is a contagious skin and parasitic disease. It is caused by the scabies mite, which is a parasitic mite. A person can become infected either through close contact with the skin of an infected person or through bed linen, towels, clothing or, for example, an upholstered chair. "For example, it is enough to use the same towel as a sick person, in a school environment, for example, to borrow a classmate's jacket, gloves, or to throw clothes into a single pile in a common locker room. The scabies mite survives on a contaminated object in a suitable environment for one to three days and can burrow into the skin of its new host in just two to three minutes," noted Fabiánová.
People notice the first symptoms two to six weeks after infection. Two red circles appear on sensitive areas of the skin, with a connector (like small dumbbells) between them.
The person concerned has itchy skin, especially after warming up in bed or taking a bath. "Scabies occurs mainly in areas with a thinner layer of skin," Fabiánová pointed out. This means on the wrists, between the fingers, on the genitals, on the areolas of the nipples, in the navel or waist area, on the inner surfaces of the thighs or on the ankles. In children, on the scalp, on the palms or soles of the feet.
Scabies, which affects up to three hundred million people worldwide each year, can infect anyone of any age or nationality. It is most common in tropical areas, but it also has fertile ground in other places with a greater number of people. Classically, for example, in schools, hospitals or hostels. However, it can also appear in luxury hotels . "Many of us associate scabies with poor hygiene, but anyone can contract the disease. We also had a patient who stayed in one of the best Munich hotels and became infected there," Monika Arenbergerová from the Dermatovenerology Clinic of the Královské Vinohrady University Hospital in Prague said.
To cure scabies, doctors prescribe special ointments and creams, and the patient has to undergo treatment for weeks.