Dengue fever
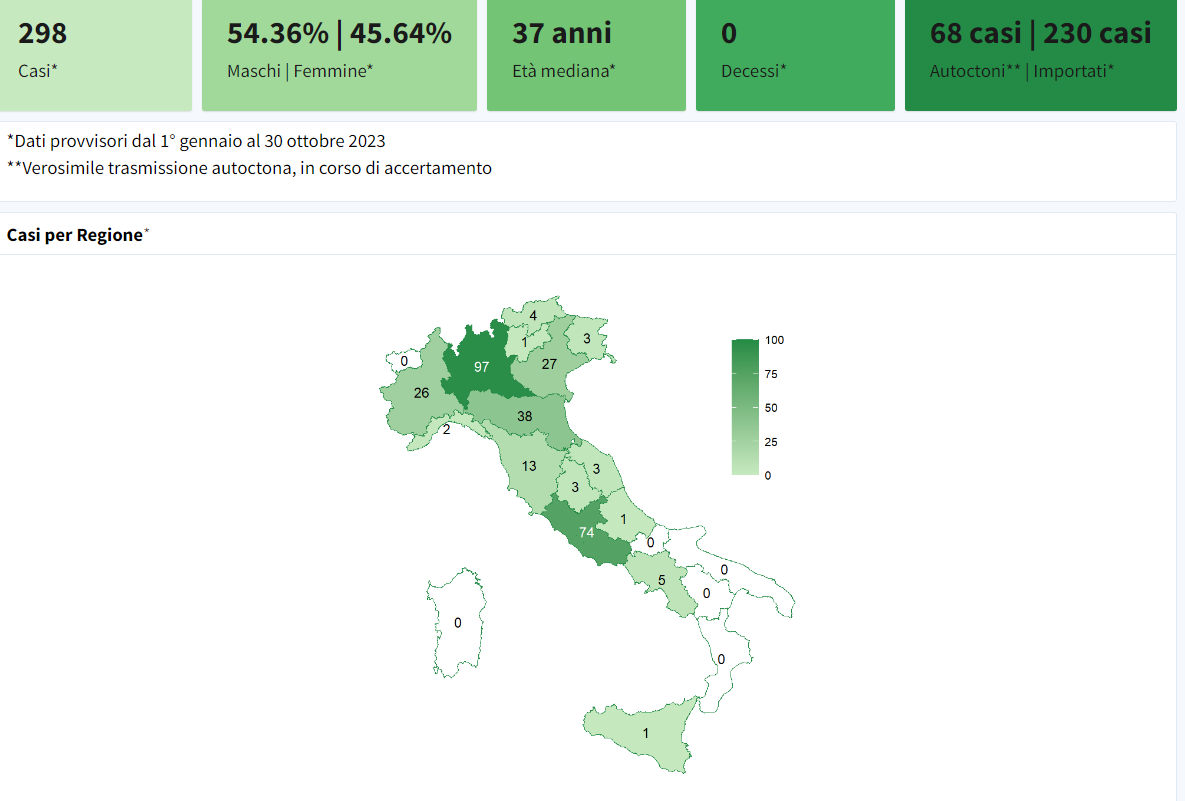
According to Italian health authorities, there are 68 locally transmitted dengue infections in the country through October 30.
These cases include four unconnected transmission episodes in the province of Lodi (36 confirmed cases), in the province of Latina (2 cases) and in the province of Rome (29 cases with exposures in different parts of the metropolitan city of Rome and 1 case in Anzio, for which investigations are underway to verify any epidemiological links).
All cases, whose outcome is known, have recovered or are improving.
Since the beginning of the year, 230 cases of dengue imported from other countries have also been reported.
Dengue is caused by four very similar viruses (Den-1, Den-2, Den-3 and Den-4) and is transmitted to humans by mosquito bites which, in turn, bite an infected person . There is no human-to-human transmission.
The virus circulates in the blood of the infected person for 2-7 days, and in this period the mosquito can pick it up and transmit it to others. In the Western Hemisphere the main vector is the Aedes aegypti mosquito, although cases transmitted by Aedes albopictus (the so-called 'tiger mosquito') have been recorded.
Dengue has been known for over two centuries, and is particularly present during and after the rainy season in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, Southeast Asia and China, India, the Middle East, Latin and Central America, Australia and several areas of the Pacific.
In recent decades, the spread of dengue has increased in many tropical regions and outbreaks of local transmission have been confirmed in some European countries including Italy. In the countries of the northern hemisphere, particularly in Europe, it constitutes a danger from a global health perspective, given that it manifests itself above all as an imported disease (the increase in which is due to the increased frequency of movement of goods and people) and public health due to the risk of local transmission.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Dengue virus infections are normally mild, and the majority of people who contract the virus do not develop symptoms. Occasionally, however, the virus can cause a serious illness that requires medical attention. The disease causes even very high fever within 5-6 days of the mosquito bite. Fever is accompanied by headache, pain around and behind the eyes, severe muscle and joint pain, nausea and vomiting, skin irritations that may appear on most of the body 3-4 days after the onset of fever. Typical symptoms are often absent in children. The diagnosis is normally suspected based on the symptoms, but is confirmed with laboratory tests aimed at looking for the virus or specific antibodies in blood samples.
Subscribe to Outbreak News TV on YouTube
West Nile virus
Since the beginning of May, 322 confirmed cases of West Nile Virus (WNV) infection in humans have been reported in Italy.
Of these, 183 occurred in the neuro-invasive form (37 Piedmont, 55 Lombardy, 21 Veneto, 2 Friuli-Venezia Giulia, 1 Liguria, 54 Emilia-Romagna, 6 Puglia, 1 Calabria, 1 Sicily, 3 Sardinia) 2 imported cases (1 Hungary, 1 France), 70 asymptomatic cases identified in blood donors (13 Piedmont, 33 Lombardy, 4 Veneto, 1 Friuli-Venezia Giulia, 16 Emilia-Romagna, 1 Campania, 1 Puglia) 1 imported case (Germany), 68 cases of fever (5 Piedmont, 20 Lombardy, 36 Veneto, 6 Emilia-Romagna, 1 Puglia) and 1 asymptomatic case (Lombardy).
Among the confirmed cases, 21 deaths have been reported (5 Piedmont, 11 Lombardy, 1 Friuli-Venezia Giulia, 4 Emilia-Romagna).
West Nile Fever is a disease caused by the West Nile Virus (WNV), a virus of the Flaviviridae family isolated for the first time in 1937 in Uganda, precisely in the West Nile district (from which takes its name). The virus is widespread in Africa, Western Asia, Europe, Australia and America.
The reservoirs of the virus are wild birds and mosquitoes (most frequently of the Culex genus), whose bites are the main means of transmission to humans. Other documented means of infection, although much rarer, are organ transplants, blood transfusions, and mother-to-fetus transmission during pregnancy.
Dengue News Today: Italy and France top 100 local cases, Sri Lanka, Mexico and more
West Nile fever is not spread from person to person through contact with infected people. The virus also infects other mammals, especially horses, but in some cases also dogs, cats, rabbits and others. In Italy for several years now, a few dozen cases of West Nile have occurred in the summer period (up to a few hundred in the years with higher incidence), transmitted by mosquito bite, while no cases of transmission by transfusion or transplant have ever been documented.
Incubation and symptoms
The incubation period from the moment of the bite of the infected mosquito varies between 2 and 14 days, but can also be 21 days in subjects with immune system deficiencies. Most infected people do not show any symptoms.
Among symptomatic cases, approximately 20% present symptoms such as fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, swollen lymph nodes, skin manifestations. These symptoms can last a few days, in rare cases a few weeks, and can vary greatly depending on the age of the person. In children, a mild fever is more frequent, while in young people the symptoms are characterized by medium-high fever, redness of the eyes, headache and muscle pain. In the elderly and debilitated people, however, the symptoms can be more serious.
The most serious symptoms occur on average in less than 1% of infected people (1 in 150 people) and include high fever, severe headaches, muscle weakness, disorientation, tremors, visual disturbances, drowsiness, convulsions, up to paralysis and coma. Some neurological effects may be permanent. In the most serious cases (about 1 in a thousand) the virus can cause lethal encephalitis.






Thank you!
Thanks for this article!