Parasitology 101 is an educational blog that that can be used as a study guide for microbiology, infectious disease and medical technology students. The “bullet-point” format keeps the information concise and to the point.
General Information
Also known as “Fish Tapeworm” and “Broad Tapeworm”
Largest human tapeworm, strobila can reach 30-45 ft in length
Geography
Worldwide, particularly in cool lake regions of the Northern hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia) and South America
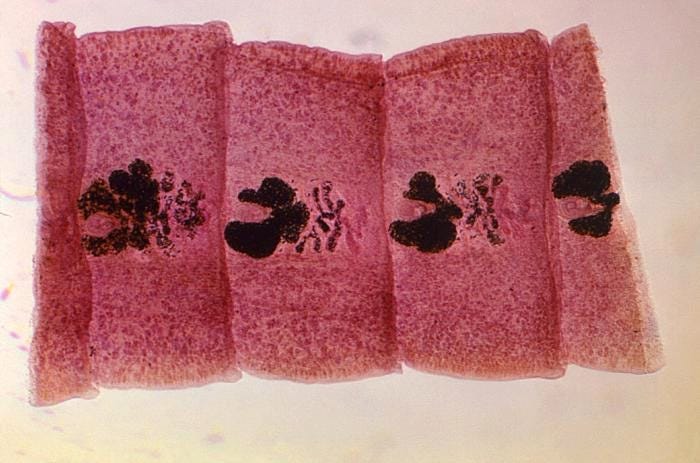
Morphology (adults)
30-45 ft in length, 1 cm in width
Scolex (head) spatulate with two slit-like grooves (bothria)
3000 proglottids, each with “rosette-shaped” uterus.
Proglottids wider than long
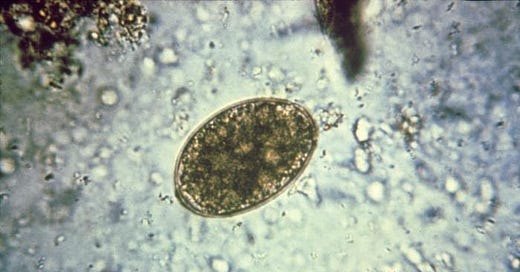
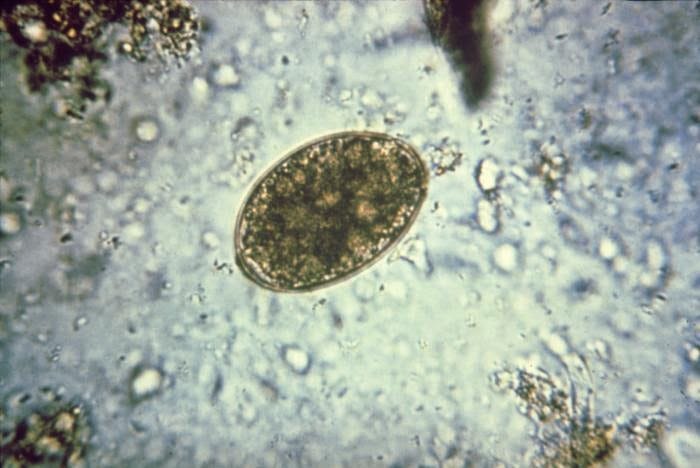
Morphology (eggs)
Oval or ellipsoidal, 75 um x 45 um
Operculated
Undeveloped embryo (coracidium)
Small, terminal abopercular knob
Life Cycle
Adult in small intestine
Immature eggs shed from gravid proglottids, passed in feces
Eggs develop in fresh water> develop into coracidium
Coracidium emerge from egg, ingested by freshwater crustacean (copepod, Cyclops sp.) First intermediate host
Develops into procercoid larva
Infected crustacean ingested by small freshwater fish (minnows for example) (second intermediate host)> develops into plerocercoid larva (sparganum)
Infected small fish ingested by larger “predatory fish” (perch, trout, etc)> plerocercoid larva released and penetrates muscles of predator fish
Humans infected when consuming raw or undercooked infected fish
Plerocercoid larva develops to adult in small intestine
From beginning of infection> approximately 6 weeks until eggs passed in feces
Adult can live for up to 20 years, each adult can shed 1 million eggs/day
Pathology
Usually asymptomatic, patient becomes aware when worm segments passed in stool
Clinical manifestations may include pernicious anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency
Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, vomited, weight loss
Heavy infections can result in intestinal obstruction
Diagnosis
Microscopic identification of eggs in stool sample. Examination of characteristic proglottids also useful.
Treatment
Praziquantel or nicolsamide
Epidemiology
Freshwater transmission dependent on available human/mammal definitive host, suitable intermediate hosts, consumption of raw or undercooked freshwater fish
Pollution of freshwater with infected human feces
Prevention
Thorough cooking of freshwater fish, or
Freezing fish for 24 hours at -18C (0F), or
Irradiation