Parasitology 101 is an educational blog that that can be used as a study guide for microbiology, infectious disease and medical technology students. The “bullet-point” format keeps the information concise and to the point.
General Information
Human intestinal trematodiases are associated with eating habits
They are localized to areas where there is water, snail vectors and reservoir hosts
Geography
Widely found in rural southeast Asia, in particular central and south China, parts of India and Thailand
Morphology (adults)
Fasciolopsis buski is the largest fluke to infect humans, aka Giant Intestinal Fluke
7.0 x 1.5 cm
Large, leaf-shaped, lacks a cephalic cone
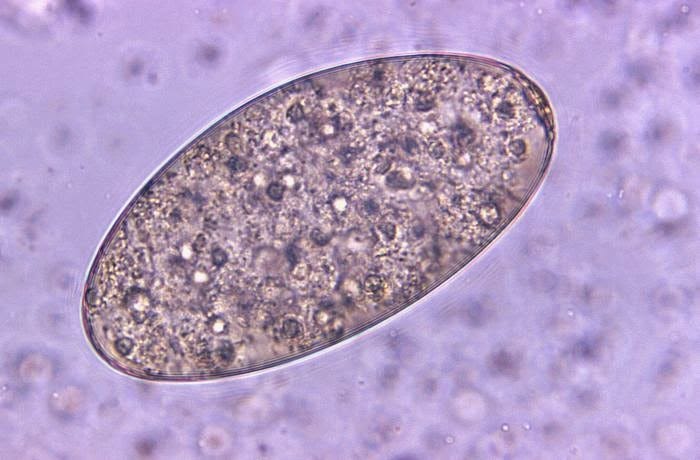
Morphology (eggs)
Large, thin-shelled, unembryonated, operculated
130-150 x 78-98 um
Found in large numbers in feces, too similar to F. hepatica to differentiate
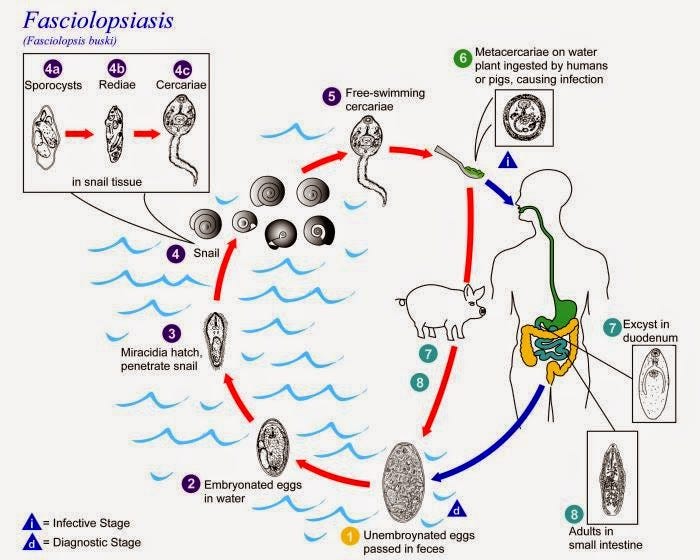
Life Cycle
Adults in the small intestine
Eggs pass in feces to water where they embryonic
After few weeks, miracidium emerges
Miracidium swims to find suitable snail (Segmentina sp.) as first intermediate host
In the snail-sporocysts>rediae>cercariae
Cercariae released from snail to water
Encyst on aquatic plant as metacercariae
Plant eaten raw by mammalian host (humans and pigs)
Metacercariae excysts and attach to the gut mucosa
Develop into adults in about 3 months
Lives for one year
Pathology
More worms, more disease- usually asymptomatic
Large number of worms attaching to mucosa – bleeding, inflammation and ulceration
Diarrhea (foul smelling greenish-yellow stools), abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction, edema
Toxic products from worms may be absorbed and cause toxemia
Death is rare
Diagnosis
Travel history
Demonstration of eggs in feces or vomit (eggs indistinguishable from F. hepatica)
Rarely by identifying adult fluke
Subscribe to Outbreak News TV on YouTube
Treatment
Praziquantel is the drug of choice
Epidemiology
Pigs are reservoir hosts
Metacercariae encysts on hard surface, particularly water plants like water caltrop and water chestnuts
The outer cover of plant is peeled off with teeth and metacercariae are released into the mouth
Children more frequently infected–eat water plants going to and from school
Prevention
Treatment
Education
Changing eating habits- do not eat without boiling first
Keep pigs from contaminating areas where water plants grow
Do not feed water plants to pigs