Guinea reports 1st yellow fever outbreak since 2020
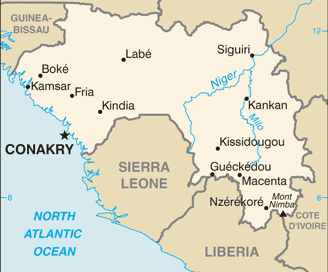
A few weeks ago, the Guinea Ministry of Health reported 178 cases (45 confirmed; 133 suspected) and four deaths (CFR: 2.2%) of yellow fever from Dabola district, Faranah region.
This outbreak was confirmed after 45 blood samples tested positive for yellow fever by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) at the National Institute of Public Heath, Conakry.
The confirmed cases presented with symptoms of fever, jaundice and fatigue.
The last outbreak of yellow fever in Guinea was in December 2020, with 48 suspected cases and 14 deaths reported from three regions: Boké, Kankan and Kindia.
Elsewhere in Africa this year, a total of 3,040 cases (406 confirmed; 2,634 suspected) and 29 deaths (CFR: 1.0%) of yellow fever have been reported in seven African countries, including the above data from Guinea: Cameroon (43 cases; 3 deaths), Central African Republic (326; 5), Congo (598; 0), Gabon (64; 0), Guinea (178; 4), Nigeria (1,819; 21) and Uganda (12; 0).
Yellow fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic fever. Yellow fever virus spreads through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
Yellow Jack: How Yellow Fever Ravaged America and Walter Reed Discovered Its Deadly Secrets
Symptoms of yellow fever (fever, chills, headache, backache, and muscle aches) develop 3-6 days after infection. About 15% of people infected with yellow fever virus will develop severe illness that can lead to liver disease, bleeding, shock, organ failure, yellowing skin (jaundice), and sometimes death.
Subscribe to Outbreak News TV on YouTube
To prevent getting sick from yellow fever, use insect repellent, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants, and get vaccinated.