Scabies is spreading rapidly in the Czech Republic reporting 4413 cases since the beginning of this year. The number of people with scabies in the country has been increasing since 2023 (9167) and 2024 (8991).
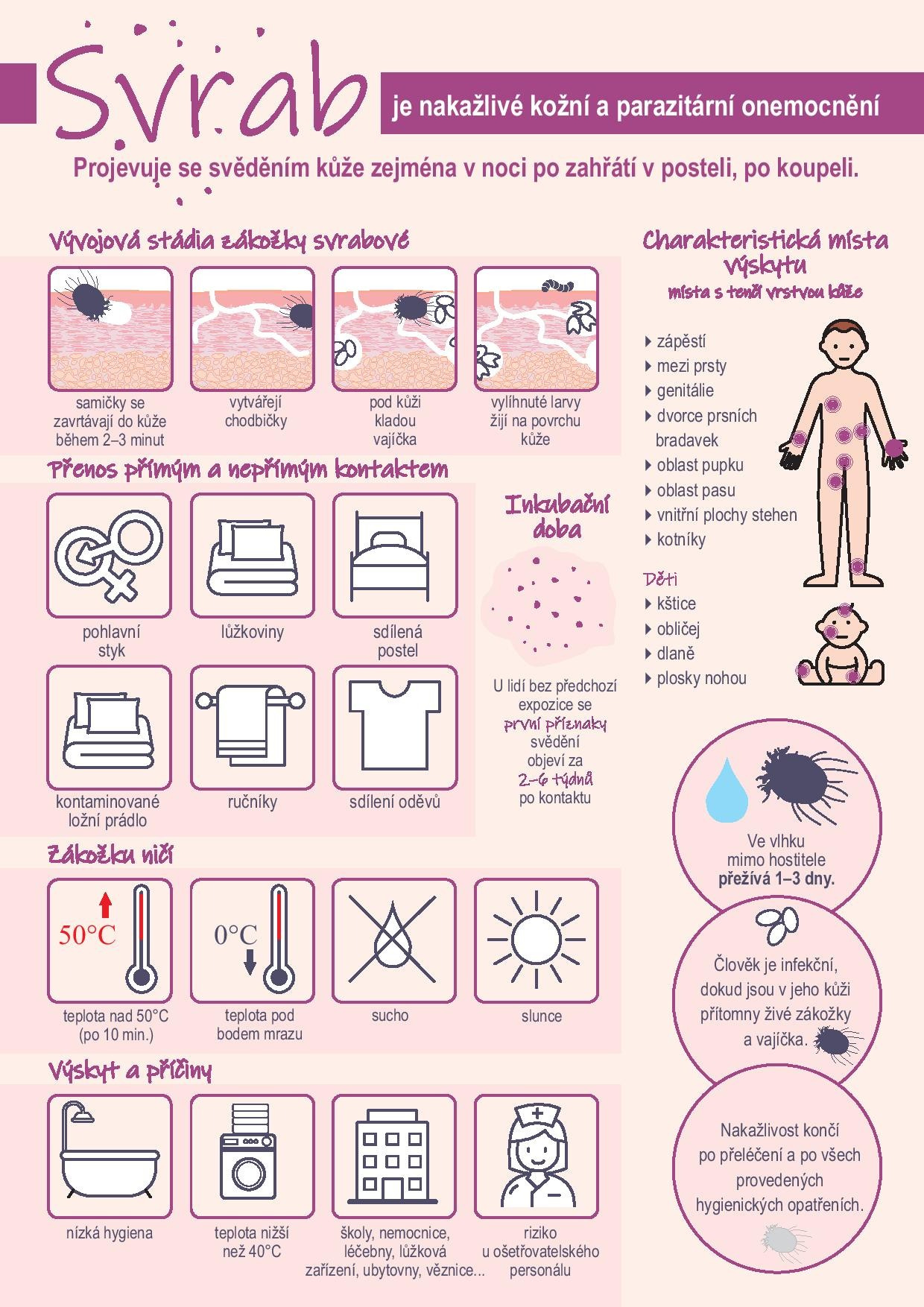
The disease is caused by the scabies mite - a mite measuring less than half a millimeter burrows into the skin within two to three minutes, where it causes a rash and unpleasant itching.
Scabies is highly contagious. It is transmitted not only by direct skin-to-skin contact between a healthy person and an infected person (e.g. during sexual intercourse or sleeping in the same bed), but also indirectly. All it takes is contact with contaminated bed linen, towels, clothing or textiles in furniture. Anyone can become infected, regardless of age or social status.
Signs and symptoms: The clinical picture of scabies is characterized by intense itching of the skin, especially at night after warming up in bed, and the appearance of skin manifestations that are located in predilection areas with a thinner layer of skin, such as the wrists, the skin between the fingers, the genitals, the anterior axillary fold, the areola of the nipples, the navel, the waist and the inner surfaces of the thighs and the ankles. In children, skin eruptions can affect the scalp, face, palms and soles of the feet. In infants, the entire body can be affected.
Pozor na svrab - MUDr. Kateřina Fabiánová, Ph.D. pro CNN Prima NEWS
The primary lesion may be covered by acute dermatitis, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The most common complication is secondary bacterial infection, especially with beta-hemolytic streptococci of group A or Staphylococcus aureus, caused by scratching, resulting in pyoderma, post-scab pruritus, eczematous manifestations and urticaria.
The infection can cause an allergic reaction with significant swelling of the lymph nodes, which remains for several months after anti-scabies therapy. Itching of the skin can also persist for many weeks after treatment. Skin manifestations of scabies caused by animal mites appear suddenly, about 10 days after infestation by the mite. They disappear gradually, about 4-6 weeks after the end of contact with the animal.
Incubation period: The length of the incubation period depends on the level of personal hygiene and any previous illness. In people without previous exposure, the first symptoms, i.e. itching, appear 2-6 weeks after contact. In people with a high level of hygiene, the incubation period tends to be longer. In case of repeated infection, the incubation period is shorter; symptoms of the disease appear as early as 1-4 days after exposure.
Cause: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis mite (scabies mite).
Source: The source of scabies in humans is exclusively an infested person.
Transmission: usually direct, for example, through close skin contact with an infected person, especially during sexual intercourse, in a warm environment on a bed, when sleeping in the same bed, or indirectly, especially through contact with contaminated bed linen, towels or wearing clothes that have been used by an infected person. The spread of the disease is facilitated by low hygiene standards, promiscuity and institutionalization (e.g. hostels, dormitories, long-term care facilities, hospitals, psychiatric hospitals, social care institutions). Areas where a large number of people change frequently and quickly without the possibility of sufficient cleaning and changing bed linen are particularly risky. Clothes and linen that cannot be washed at temperatures higher than 40° C are problematic in terms of possible transmission.
Period of infectivity, susceptibility, immunity: The infectivity of a patient with scabies lasts as long as live mites and parasite eggs are present in his skin. It ends after a properly performed anti-scabies treatment and after all thoroughly performed hygiene measures to prevent further spread of the infection or reinfestation. Persons with previous infestation are more susceptible to repeated disease. Persons with reduced immunity are more prone to hyperinfestation. The main primary predisposing factors include overcrowding, social intimacy, population migration, low hygiene levels, malnutrition, immunological factors, especially reduced immunity, and institutionalization.
Scabies treatment: Scabies therapy is local or general. For local treatment of scabies, antiscabietics are used, i.e. ointments and creams containing substances that destroy the mites. However, these preparations must be applied thoroughly to the entire body, from the neck down. In places where the ointment is not applied, the mites can survive, so it is necessary that the preparation be applied so that it acts on the mites directly, by contact. In younger children, the face and the hairy part of the head must also be coated. After applying the entire body, hands are not washed.
The treatment course must be repeated, the preparations are applied once every 24 hours, usually for three consecutive days; a single application is not enough. During one treatment course, the patient is recommended not to wash. After each course, it is necessary to bathe, change underwear and bed linen, and boil all underwear again or treat it in the recommended way.