Parasitology 101 is an educational blog that that can be used as a study guide for microbiology, infectious disease and medical technology students. The “bullet-point” format keeps the information concise and to the point.
General Information
Beef tapeworm
Definitive host is humans, herbivores are intermediate hosts
Geography
Worldwide, particularly where beef is eaten raw or undercooked
Morphology (adults)
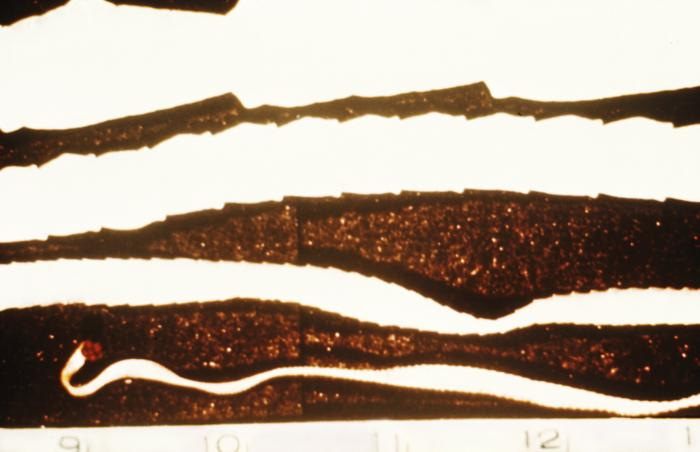
Strobila is 15-20 ft
1000-3000 proglottids
Gravid proglottids are longer than wide
Mature proglottid has 12-30 lateral uterine branches, can be differentiated from Taenia solium (7-13)
Quadrate (four suckers), unarmed scolex
Morphology (eggs)
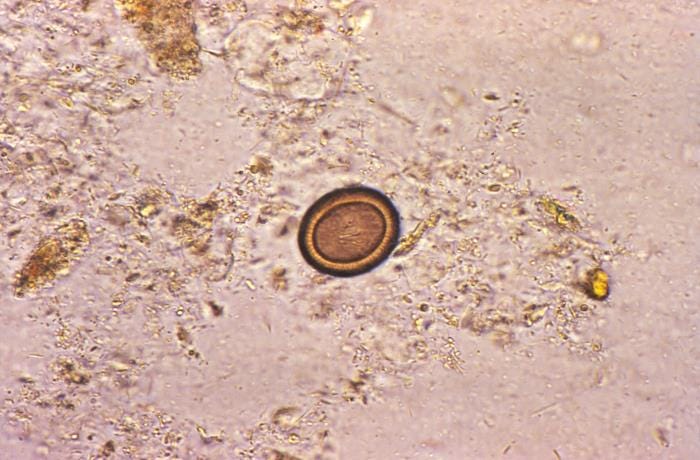
30-35 um in diameter, radial striated
Internal oncosphere contains three pairs of hooklets
Indistinguishable from Taenia solium eggs
Life Cycle
Adult in small intestine
Gravid proglottids with infective eggs passed in feces
Eggs can survive for months in the environment
Eggs ingested by cattle
Eggs hatch> onchospheres released> invade intestinal wall> becomes lodged in striated muscle
Develop into cysticerci (survive for years)
Humans are infected by eating raw or undercooked beef
Cysticerci attach to small intestine and mature to adults
Pathology
Most patients asymptomatic
Mild abdominal symptoms
Migrating proglottids- appendicitis or cholangitis possible
Diagnosis
Identification to the species level not possible based solely on microscopic exam of eggs
Egg stage a potential health hazard (T. solium)
Identification of proglottids and/or scolex
Treatment
Praziquantel or niclosamide
Epidemiology
Cattle infected while grazing on contaminated vegetation
Prevention
Cook beef thoroughly