Two Naegleria fowleri deaths reported in a week in Karachi
11 people have lost their lives so far due to Naegleria fowleri infection across Sindh province
In Pakistan, the Sindh province health department reported two deaths due to Naegleria fowleri in a week and three in the past two weeks.
The latest cases are a 45-year-old man and a 22-year-old student, the most recent death, both from North Karachi.
According to health officials, the latest victims had no history of swimming, suggesting that they might have contracted the infection during nasal rinsing.
Sindh health officials advise the public to avoid activities that may cause water to enter the nose.
Since 2012, according to health department officials, over 100 cases of Naegleria fowleri have been reported in Karachi. Of them, only one patient survived for three months. In another case reported this year, the patient recovered well and is still alive.
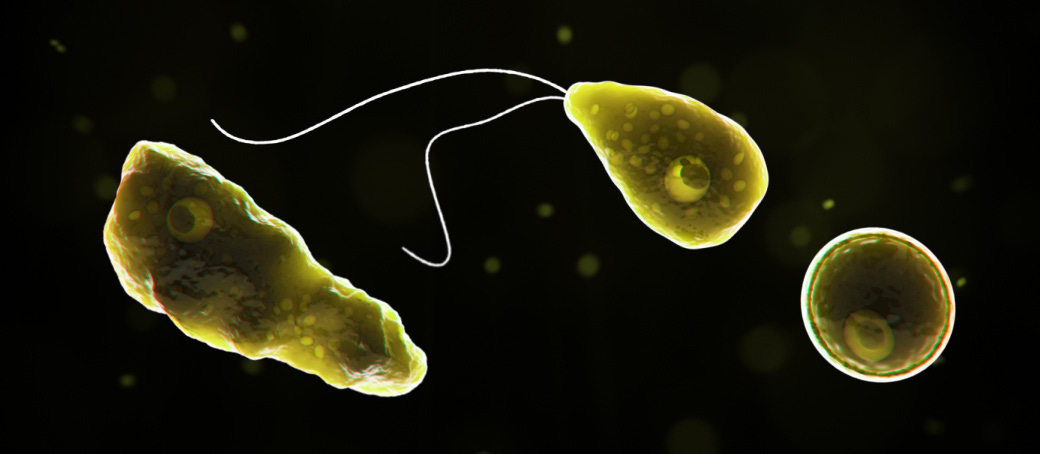
Naegleria fowleri is a microscopic amoeba which is a single-celled living organism. It can cause a rare and devastating infection of the brain called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). The amoeba is commonly found in warm freshwater such as lakes, rivers, ponds and canals.
Infections can happen when contaminated water enters the body through the nose. Once the amoeba enters the nose, it travels to the brain where it causes PAM (which destroys brain tissue) and is usually fatal. Infections usually occur when it is hot for prolonged periods of time, which results in higher water temperatures and lower water levels.
Naegleria fowleri infections are rare. Most infections occur from exposure to contaminated recreational water. Cases due to the use of neti pots and the practice of ablution have been documented.
Subscribe to Outbreak News TV on YouTube
You cannot be infected with Naegleria fowleri by drinking contaminated water and the amoeba is not found in salt water.
Initial symptoms of PAM usually start within 1 to 7 days after infection. The initial symptoms may include headache, fever, nausea, or vomiting.
Other symptoms can include stiff neck, confusion, loss of balance, seizures, and hallucinations. After the start of symptoms, the disease progresses rapidly.